The Primary Flight Display (PFD) on the Airbus A320 is a critical component of the aircraft’s Electronic Flight Instrument System (EFIS). It provides pilots with essential flight information such as attitude, speed, altitude, heading, vertical speed, and flight mode annunciations in a consolidated and intuitive format. Below is a detailed breakdown of the A320 PFD:
Layout and General Design
The PFD is organized into distinct sections, with information grouped by function. The design is optimized to reduce pilot workload and enhance situational awareness. The layout includes:
- Attitude Indicator (AI):
- Centered on the display, it shows the aircraft’s pitch and bank angles relative to the horizon.
- The artificial horizon divides the display into sky (typically blue) and ground (brown).
- A bank angle scale is displayed around the horizon, with markers at 10°, 20°, 30°, and 45°.
-Pitch Scale: Graduated in 2.5° increments near the horizon, increasing to 5° increments further out.

2.Air Speed Tape (Left side):
- Displays the aircraft’s indicated airspeed (IAS) in knots on a vertical tape.
- Markers and colors indicate key speed regions:
- Green: Normal operating range.
- Amber/Red: Overspeed or low-speed warning zones.
- Bug markers (white) show target speeds such as V1, VR, V2, or managed/selected speeds.
-Green Dot: Optimal speed for clean configuration climb.
-VLS (Lowest Selectable Speed): Amber bar indicating minimum speed for the current configuration.
-Overspeed Warning (Vmax): Red band at the top of the tape. - Trend vector: A short arrow indicates the predicted airspeed in the next 10 seconds based on current acceleration.
3.Altitude Tape (Right side):
- Displays the current altitude in feet using a vertical tape.
- Includes markers for selected altitude, transition altitude, and other relevant altitude targets.
- Barometric setting (QNH/QFE) is shown near the base of the tape.
- A trend vector indicates predicted altitude changes.
4.Heading Tape (Bottom):
- Displays the aircraft’s current heading using a rotating compass rose.
- Includes a heading bug for selected heading and course indicators for navigation guidance.
- Displays track deviation and navigation aids.
5.Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI):
- Positioned to the right of the altitude tape.
- Displays the rate of climb or descent in feet per minute (fpm).
- Trend markers indicate if the vertical speed is increasing or decreasing.
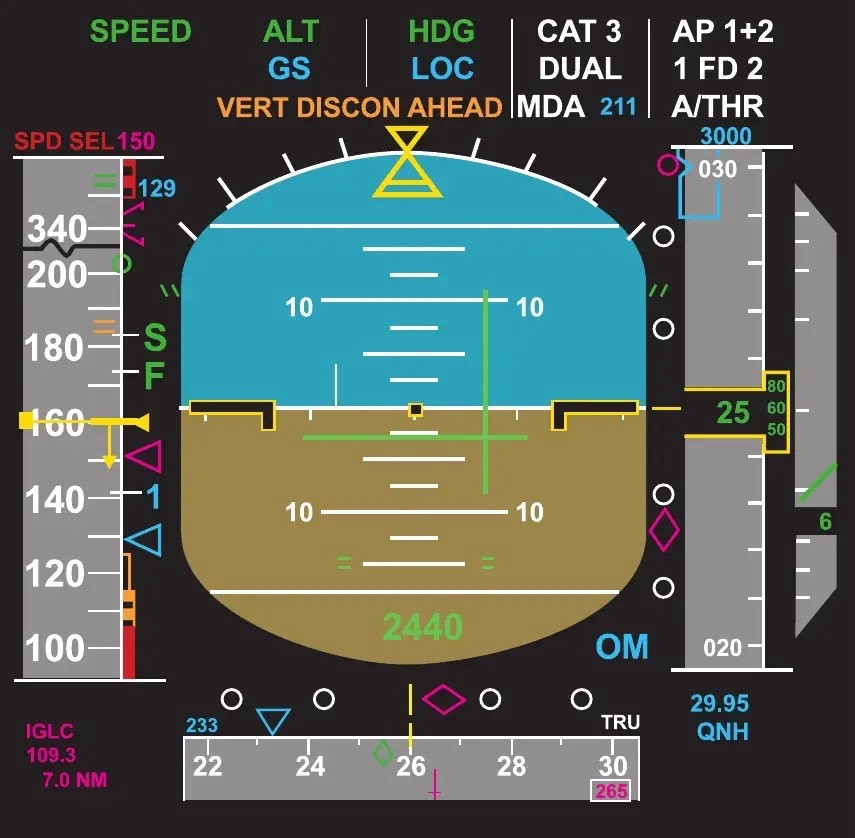
6.Flight Mode Annunciator (FMA) (Top Section):
- Shows active and armed modes for autopilot, flight directors, and autothrust.
- Divided into columns for Autothrust (A/THR), Vertical Guidance, Lateral Guidance, Approach Mode, and Other information.
Autothrust (A/THR): Modes such as SPEED, THR CLB, or MAN THR.
Vertical Modes: ALT*, ALT, V/S, etc.
Lateral Modes: NAV, HDG, LOC, etc.
Approach Modes: APP NAV, LAND, FLARE.
Other Status: Autopilot (AP1/AP2), Flight Director (FD), or autothrust status. - Colors indicate mode status:
Green: Active modes.
Blue: Armed modes.
White: Advisory or status information.
LS Button Functionality:
Activates display elements for Instrument Landing System (ILS) or Microwave Landing System (MLS) approaches. Detailed Functionality of Key Elements
Attitude Indicator - The attitude indicator is fundamental for spatial orientation.
- The pitch scale (in degrees) allows pilots to determine nose-up or nose-down angles.
- Bank angle markings, combined with a slip/skid indicator (small triangle at the bottom), help maintain coordinated flight.
Speed Awareness. The speed tape incorporates safety features: - Alpha Prot (Protection): Low-speed protection zone appears amber to warn the pilot of impending stall conditions.
- Overspeed Limitations: An overspeed warning (red band) alerts the crew to avoid structural stress or flutter.
- Speed trends help pilots anticipate changes due to configuration or environmental factors.
Altitude Awareness - Transition altitudes are highlighted, and the system alerts pilots to barometric setting mismatches during transitions.
- Selected altitudes set in the Flight Control Unit (FCU) are prominently displayed, aiding altitude adherence.
Flight Path Vector (FPV) - Located on the attitude indicator, the FPV shows the actual trajectory of the aircraft relative to the horizon.
- This helps pilots visualize where the aircraft is going in terms of altitude and lateral movement.
Heading Management - The heading tape interacts with navigation systems:
- Managed Mode: The aircraft follows a predetermined flight plan from the Flight Management System (FMS).
- Selected Mode: The pilot manually inputs headings via the FCU.

FMA
- The FMA provides real-time updates on autopilot and flight director operations:
- It distinguishes between active (engaged) and armed (standby) modes.
- Displays autothrust modes, such as SPEED (maintain speed) or THR CLB (climb thrust).
- Alerts include color changes or flashing indications when modes change or disengage.
Alerts and Warnings
- The PFD integrates seamlessly with the Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) and Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS):
- EGPWS alerts (e.g., “TERRAIN AHEAD”) appear as annunciations.
- TCAS advisories (e.g., “CLIMB” or “DESCEND”) overlay on the display.
- Stall, overspeed, or altitude deviation warnings trigger visual (flashing bands) and auditory cues.
-Alerts such as “STALL” or “WINDSHEAR” are displayed on the PFD.
Integrated Systems
The PFD on the A320 is part of a larger suite of systems: - Flight Management and Guidance System (FMGS): Provides managed mode inputs.
- Autopilot and Flight Director (AP/FD): Displays flight director bars for manual guidance or autopilot feedback.
- Automatic Flight Control System (AFCS): Works with the PFD to manage thrust, altitude, and lateral guidance.
Pilot Interface. - The PFD ensures a smooth transition between manual and automated flight.
- Pilots can adjust displayed parameters, such as barometric pressure, using physical knobs on the FCU or through MCDU (Multipurpose Control and Display Unit) inputs.
- Intuitive design aids in quickly diagnosing flight path deviations or system issues.
Redundancy and Safety - Dual PFDs are present for captain and first officer, ensuring independent functionality.
- In case of failure, the system provides backup modes through the navigation display (ND) or standby instruments.
Conclusion
The A320’s PFD is a highly intuitive, data-rich interface that supports modern aviation’s emphasis on safety and efficiency. By integrating critical flight data and providing real-time feedback, the PFD significantly enhances a pilot’s situational awareness and decision-making capabilities. Its design aligns with Airbus’ philosophy of reducing workload through automation while maintaining pilot control.
For all aviation-related guidance (DGCA ground classes, pilot training, cabin crew training)
Contact us https://contrail.in/
phone numbers +91 78457 69399


